Science
Related: About this forumMore transparent than glass, new material cools rooms and self-cleans
By Michael Irving
May 27, 2024
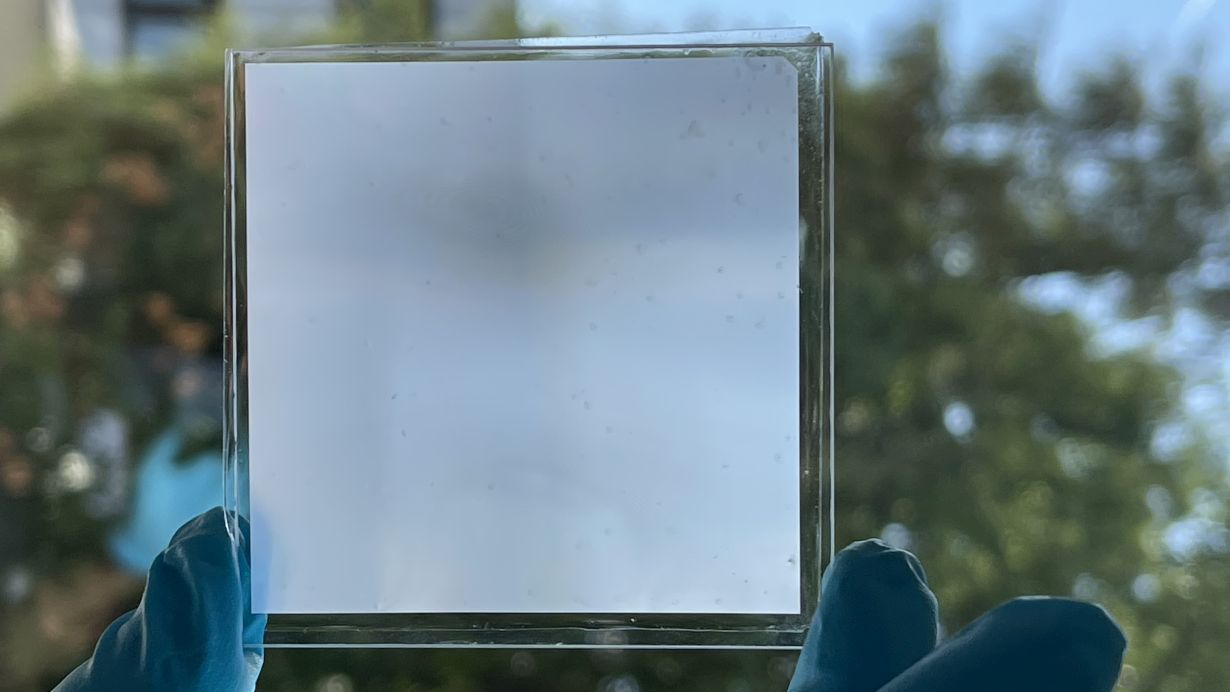
A sample of the new metamaterial, which is more transparent than glassGan Huang, KIT
VIEW 2 IMAGES
Having lots of glass surfaces can brighten up a room, but it also lets in too much heat as well as neighbors’ prying eyes. A new metamaterial is not only more transparent to light, but adds privacy, cools the room inside, and automatically cleans itself.
Known as a Polymer-based Micro-photonic Multi-functional Metamaterial (PMMM), the team’s creation takes the form of a thin film that can be stuck onto a pane of regular glass. It gets its special properties from the microscopic structure of its surface, which is etched with a pattern of pyramids each just 10 microns wide.
These mini-pyramids scatter 73% of the light that hits them, which gives the material that frosted look. But despite that, it’s surprisingly more transparent to light than regular glass – 95% transmittance compared to the usual 91% of most glass. The team says that makes for a more comfortable lighting not just for people, but plants as well.
“When the material is used in roofs and walls, it allows for bright yet glare-free and privacy-protected indoor spaces for work and living,” said Gan Huang, lead author of the study. “In greenhouses, the high light transmittance could increase yields because the photosynthesis efficiency is estimated to be 9% higher than in greenhouses with glass roofs.”
More:
https://newatlas.com/materials/metamaterial-glass-radiative-cooling-self-cleaning/
Judi Lynn
(164,050 posts)I have been sick about birds vs. windows for a very long time.
Bernardo de La Paz
(60,320 posts)I've only skimmed (time), but this is interesting.
If applied inside, there would be some reflection off the outside (sky, clouds) but it would seem dulled due to the back scatter from the inside film. That would probably reduce bird strikes significantly.
If applied to the outside, I think it would eliminate reflections and bird strikes would be dramatically reduced, perhaps close to zero.
But I do not see it being applied over all windows on office towers. An idea would be to apply it on all but leave a clear band from
4 1/2 to 6 feet high. Residential towers might do that too, except perhaps for one window per unit completely clear for people to sit and admire views.
NoRethugFriends
(3,653 posts)Transparent means see through.
Diraven
(1,840 posts)A lot of people mix those up.
Metaphorical
(2,597 posts)Transparency means that you can see through it. Translucent means that light can penetrate, but it's scattered and diffuse.
Judi Lynn
(164,050 posts)Published: 07 May 2024
Abstract
Transparent roofs and walls offer a compelling solution for harnessing natural light. However, traditional glass roofs and walls face challenges such as glare, privacy concerns, and overheating issues. In this study, we present a polymer-based micro-photonic multi-functional metamaterial. The metamaterial diffuses 73% of incident sunlight, creating a more comfortable and private indoor environment. The visible spectral transmittance of the metamaterial (95%) surpasses that of traditional glass (91%). Furthermore, the metamaterial is estimated to enhance photosynthesis efficiency by ~9% compared to glass roofs. With a high emissivity (~0.98) close to that of a mid-infrared black body, the metamaterial is estimated to have a cooling capacity of ~97 W/m2 at ambient temperature. The metamaterial was about 6 °C cooler than the ambient temperature in humid Karlsruhe. The metamaterial exhibits superhydrophobic performance with a contact angle of 152°, significantly higher than that of glass (26°), thus potentially having excellent self-cleaning properties.
Introduction
The utilization of transparent roofs and walls in buildings has gained significant attention as an effective means of harnessing natural light, reducing energy consumption1,2, and improving occupants’ well-being3,4. The integration of transparent roofs and walls in architectural design offers numerous advantages, such as maximizing daylight utilization and creating visually appealing spaces. Natural light has been shown to positively impact human health and productivity5, leading to improved comfort and mood. In addition, transparent roofs and walls contribute to energy efficiency by reducing the need for artificial lighting6, thus playing a crucial role in achieving sustainable building certifications and meeting stringent energy performance standards. Green building rating systems, such as leadership in energy and environmental design, prioritize the integration of daylighting strategies and the optimization of natural light penetration7.
Despite the clear benefits of transparent roofs and walls, traditional glass materials face inherent limitations. Glare, caused by the direct transmission or reflection of sunlight, can lead to discomfort, eye strain, and reduced visual clarity8,9. This can significantly impact productivity and overall well-being, especially for individuals who work in environments with excessive sunlight or bright lighting. Privacy concerns arise due to the transparency of traditional glass, particularly in buildings with sensitive functions such as hospitals. Additionally, the issue of excessive heat accumulation inside the building during the summer months necessitates effective heat control mechanisms to ensure a thermally comfortable indoor environment, especially for buildings located in hot, arid countries with many clear sky days. Buildings with transparent roofs and walls consume more electricity for the air conditioning systems compared to normal buildings.
To effectively minimize glare and privacy concerns, one solution is the use of light-diffusing films (LDF) to convert the direct beam of sunlight into diffuse radiation. LDFs are commonly made by suspending polymer films with transparent micro- or nanoparticles10,11,12. For example, a combination is polymethyl methacrylate suspended with silica nanoparticles10,11. By incorporating a 20% volume of silica nanoparticles, the resulting diffuse transmittance can range from 20% to 40%10. LDFs typically have a blurry appearance, which helps protect privacy. Porous films and surface-structured films have also proven to be effective LDF materials13,14. The diffuse light can also be collected by luminescent materials and transmitted towards photovoltaic cells for electricity generation15 and fostering heightened photosynthesis rate16. Recent advancements in surface engineering have led to the development of self-cleaning coatings for transparent roofs and walls. Researchers have explored the use of superhydrophobic coatings with micro- and nanostructured surfaces, which repel water and prevent the accumulation of dirt and pollutants17,18,19.
More:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-48150-2
Response to Judi Lynn (Original post)
Judi Lynn This message was self-deleted by its author.
live love laugh
(16,211 posts)msongs
(73,123 posts)Permanut
(8,043 posts)Another amazing science lesson. Thank you!