Welcome to DU!
The truly grassroots left-of-center political community where regular people, not algorithms, drive the discussions and set the standards.
Join the community:
Create a free account
Support DU (and get rid of ads!):
Become a Star Member
Latest Breaking News
Editorials & Other Articles
General Discussion
The DU Lounge
All Forums
Issue Forums
Culture Forums
Alliance Forums
Region Forums
Support Forums
Help & Search
Anthropology
Related: About this forumGenetic analysis of ancient massacre reveals instance of indiscriminate killing
From phys.org
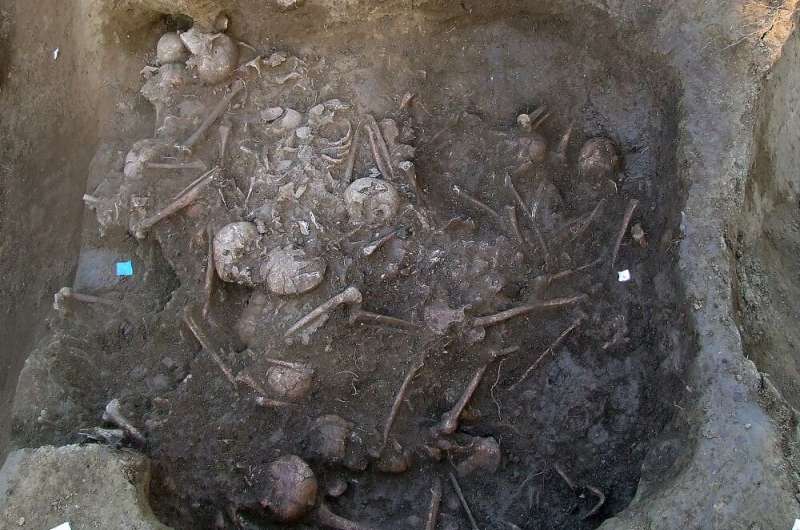

Genetic analysis provides clarity and also prompts further questions around an ancient massacre in Potočani, Croatia, in a study published March 10, 2021 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Mario Novak from the Institute for Anthropological Research, Croatia, Ron Pinhasi from the University of Vienna, Austria, David Reich from Harvard Medical School and Harvard University, U.S., and colleagues.
To date anthropological and genomic analysis of early massacres has revealed cases where the victims were plausibly killed due to battle, in-versus-out-group conflicts (such as targeting of specific families or recent migrants), or religious ritual. The massacre of 41 individuals in Potočani, Croatia, 6,200 years ago described in this study, one of the largest-scale genetic analysis of an ancient massacre to date, marks an instance of indiscriminate killing at a large scale.
The authors were able to retrieve genomic data from the bones of 38 of the 41 individuals found buried in a mass grave at Potočani, Croatia, radiocarbon dated to 4,200 years cal BCE and belonging to the Lasinja culture of the Middle Eneolithic (Copper Age).
A combination of genetic and morphological analysis revealed the grave held individuals from both sexes (21 males and 20 females) and spanning age groups: over half of the sample (21) consisted of subadults (two younger children aged between two and five years, nine older children aged between six and 10 years, and 10 adolescents aged between 11 and 17 years. Of the remaining 20 adults, 14 individuals were aged between 18 and 35 years and five between 36 and 50 years, and one adult's age at death could not be determined accurately. The genetic analysis also revealed that while some individuals in the grave were linked by family ties (eg a younger man, his two young daughters, and his nephew (brother's son) were all found in the pit), the majority of individuals (70 percent) were unrelated and instead appear to be a sample of what was clearly a large pastoral population. Interestingly, though not linked in most cases by close kin-ties, genetic evidence shows the individuals found in this grave all shared homogenous ancestry (predominantly Anatolian Neolithic with ~9% Western European hunter-gatherer ancestry), indicating the local population was large and stable—and making it unlikely that the massacre was linked to the arrival of a new, genetically-unrelated group. Though there's no way to know for sure with the evidence currently available, the authors suggest a possible reason for the massacre as potentially due to a combination of adverse climactic conditions and/or a significant increase in population size.
a little bit more ...
2 replies
 = new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
= new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
Genetic analysis of ancient massacre reveals instance of indiscriminate killing (Original Post)
Jim__
Mar 2021
OP
Baitball Blogger
(52,049 posts)1. They were sacrified because their numbers were too large?
Jim__
(15,158 posts)2. I'd take that as a "maybe."
From the original paper:
...
The mass burial from Potočani is a result of indiscriminate killing of an unrelated subset of a population with no sex and age bias, rather than a battle between two armed forces. This hypothesis is based on the demographic composition of the Potočani assemblage that includes both sexes and various age groups completely differing from the distribution seen in battle-related assemblages where younger/middle-aged males are predominant [36–41]. In terms of demographic distributions it is obvious that the Potočani assemblage is almost identical to other prehistoric massacres like Talheim [7], Asparn/Schletz [8], Schöneck-Kilianstädten [11] and Koszyce [13], but also to more recent examples [42–44] where whole or parts of communities were wiped out. The reasons for the upsurge of mass violence as well as the occurrence of massacres during the Neolithic (and Eneolithic) in Europe are “complex and multifactorial” [11]. Nevertheless, the combination of adverse climatic conditions and significant increase in population size is usually provided as the most probable reason for this phenomenon [8, 12, 45].
...
8. Teschler-Nicola M, Gerold F, Bujatti-Narbeshuber M, Prohaska T, Latkoczy C, Stingeder G, et al. Evidence of genocide 7000 BP—Neolithic paradigm and geoclimatic reality. Coll Antropol. 1999; 23: 437–450. pmid:10646219
12. Meyer C, Knipper C, Nicklisch N, Münster A, Kürbis O, Dresely V, et al. Early Neolithic executions indicated by clustered cranial trauma in the mass grave of Halberstadt. Nat Commun. 2018; 9: 2472. pmid:29941965
45. Gronenborn D, Strien H-C, Dietrich S, Sirocko F. ‘Adaptive cycles’ and climate fluctuations: A case study from Linear Pottery Culture in western Central Europe. J Archaeol Sci. 2014; 51: 73–83.
The mass burial from Potočani is a result of indiscriminate killing of an unrelated subset of a population with no sex and age bias, rather than a battle between two armed forces. This hypothesis is based on the demographic composition of the Potočani assemblage that includes both sexes and various age groups completely differing from the distribution seen in battle-related assemblages where younger/middle-aged males are predominant [36–41]. In terms of demographic distributions it is obvious that the Potočani assemblage is almost identical to other prehistoric massacres like Talheim [7], Asparn/Schletz [8], Schöneck-Kilianstädten [11] and Koszyce [13], but also to more recent examples [42–44] where whole or parts of communities were wiped out. The reasons for the upsurge of mass violence as well as the occurrence of massacres during the Neolithic (and Eneolithic) in Europe are “complex and multifactorial” [11]. Nevertheless, the combination of adverse climatic conditions and significant increase in population size is usually provided as the most probable reason for this phenomenon [8, 12, 45].
...
8. Teschler-Nicola M, Gerold F, Bujatti-Narbeshuber M, Prohaska T, Latkoczy C, Stingeder G, et al. Evidence of genocide 7000 BP—Neolithic paradigm and geoclimatic reality. Coll Antropol. 1999; 23: 437–450. pmid:10646219
12. Meyer C, Knipper C, Nicklisch N, Münster A, Kürbis O, Dresely V, et al. Early Neolithic executions indicated by clustered cranial trauma in the mass grave of Halberstadt. Nat Commun. 2018; 9: 2472. pmid:29941965
45. Gronenborn D, Strien H-C, Dietrich S, Sirocko F. ‘Adaptive cycles’ and climate fluctuations: A case study from Linear Pottery Culture in western Central Europe. J Archaeol Sci. 2014; 51: 73–83.
The full articles at references 8 and 12 are available to be read, the one at 45 is behind a paywall.